| Uploader: | Socomjunky.Com |
| Date Added: | 08.12.2016 |
| File Size: | 9.79 Mb |
| Operating Systems: | Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/2003/7/8/10 MacOS 10/X |
| Downloads: | 26598 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
Standard Normal Distribution Formula | Calculation (with Examples)
The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution of standardized values called z-scores. Because this is a standard graph, it is not made to display any particular data, it is specifically designed to show a normal curve with the mean and all standard deviations. For example, if the distribution of raw scores if normally distributed, so is the distribution of z-scores. The mean of any SND always = 0. The standard deviation of any SND always = 1. Therefore, one standard deviation of the raw score (whatever raw value this is) converts into 1 z-score unit. To find the probability of z-score, refer the column value for and row value for in the negative values of standard normal distribution. The point where the column & row values met at is the probability or critical value of Z. Similarly for two tailed Z-test, Z is the two tailed distribution. To find the probability.

Free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores
A positive z-score is to the right of the mean, and a negative z-score is left of the mean. Knowing how far a score is from the mean will give you a picture of that specific point in relation to the entire data set. If you score 1, free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores. Standard deviations and z-scores free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores a much more in depth analysis and interpretation of data.
The next time you see a report in which standard deviations are used, how much better will you understand the data? Click here to download an accessible PDF transcript. The continuous distribution is the most important of all the distributions. Its graph is bell-shaped, and you will see the bell curve in almost all disciplines.
Some of these free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores psychology, business, economics, the sciences, nursing, and, of course, mathematics. Some of your instructors may use the normal distribution to help determine your grade. Most IQ scores are normally distributed. Often, real-estate prices fit a normal distribution. The normal distribution is extremely important. In this lesson, you will study the normal distribution, the standard normal distributionz-scores, and the empirical rule.
The normal distribution has two parameterstwo numerical descriptive measures, the mean, and the standard deviation. The following graph is an example of normal distribution. It is tall in the center and fades away on either end. The right and left sides are sometimes referred to as the tails. The normal distribution is perfectly symmetrical.
The right side is the mirror image of the left side, free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores. There are three standard deviations to the right and three to the left of the center.
The mean value is expressed by the Greek letter mu,and the standard deviation is expressed by the Greek letter sigma. It will be important to remember those letters. The graph shown below is labeled with the mean in the center and standard deviations to the right and left of the center.
It is a graph of standard normal distribution. The standard normal distribution is a normal distribution of standardized values called z-scores. Because this is a standard graph, it is not made to display any particular data, it is specifically designed to show a normal curve with the mean and all standard deviations. It can be used to determine how usual or unusual a data point may be. A z-score is measured in units of standard deviation, and tells us how far away a value is from zero in standard deviations.
The z-score for a data point is found by using a simple formula. If we let x stand for any data point, the z-score is equal to x — the mean divided by the standard deviation.
Substitute the values into the formula and solve. This means the data point 8 is 1 standard deviation away from the mean, and it is one standard deviation to the right. If the z-score had been a negative, it would mean the data point was one standard deviation to the left of the mean. Values of x that are larger than the mean have positive z-scores, and values of x that are smaller than the mean have negative z-scores, free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores.
If x equals the mean, then x has a z-score of zero. By itself, this may not seem important, but when compared with other data, it can become significant. Some doctors believe that a person can lose five pounds, on the average, in a month by reducing his or her fat intake and by exercising consistently. Suppose weight loss has a normal distribution. Use a standard deviation of two pounds. See if you can answer the following questions.
Suppose a person lost ten pounds in a month. Suppose a person gained three pounds a negative weight loss. This rule is designed to draw attention to the percentages of each data population that lies in each standard deviation.
The empirical rule is also known by remembering the percentages of data in each group, the 68, 95, It is difficult to compare things that are not on the same scale.
For example, it would be hard to compare a person who lived in the s to a person who lived in the s. Their lives were very different, and the choices they made were based on very different information.
They are not on the same free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores. However, if we find two data sets that can be normally distributed, we can do that comparison with z-scores, even if they are not on the same scale. They have different instructors, but the same textbooks and similar tests.
They study together and then compare grades. Student A scored 82 on the test. The class mean on the test was 79, with a standard deviation of 2.
Student B scored 78 on the test with a class mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 1. Who scored higher relative to the other students in their class? The z-score will allow us to find the answer and definitively say which student scored a higher grade. Student A: Test grade, Mean, Standard deviation, 2. By examining z-scores, we can see that Student B is further above the mean for his class than Student A.
You can take this quiz as many times as you like. You have reached 0 of 0 point s0. If we find two data sets that can be normally distributed, we can do the comparison with z-scores, even if they are not on free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores same scale.
A video offering an example of an attractiveness score and how to determine the z-scores from the raw scores. Authored and curated by Kathryn R. Price, M. Title: Introductory Statistics — Introduction. License: CC BY 4. Skip to content. Normal Distribution and Z-Scores.
Lesson Content. Standard deviations are measures of how far any data. Read: Normal Distributions and Z-Scores Overview The continuous distribution is the most important of all the distributions, free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores. Normal Distribution The normal distribution has two parameterstwo numerical descriptive measures, the mean, and the standard deviation.
The mean, median. Reflect: Above Average? Results Vote. Expand: Comparing Data Sets Discover It is difficult to compare things that are not on the same scale. Student B: Test grade, Standard deviation, 1.
Time limit: 0. Quiz-summary 0 of 3 questions completed Questions: 1 2 3. You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again. You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You must first complete the following:. Results Quiz complete. Results are being recorded. Answered Review.
Question 1 of 3. The two parameters that define the normal distribution are…. Which Greek letter is used to represent the mean? Lesson Resources. Lesson Glossary Terms. I agree to the privacy policy. Test student assessment.
Public Domain. Figure 6.
Z Scores and Normal Distributions (Example Problems)
, time: 6:18Free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores
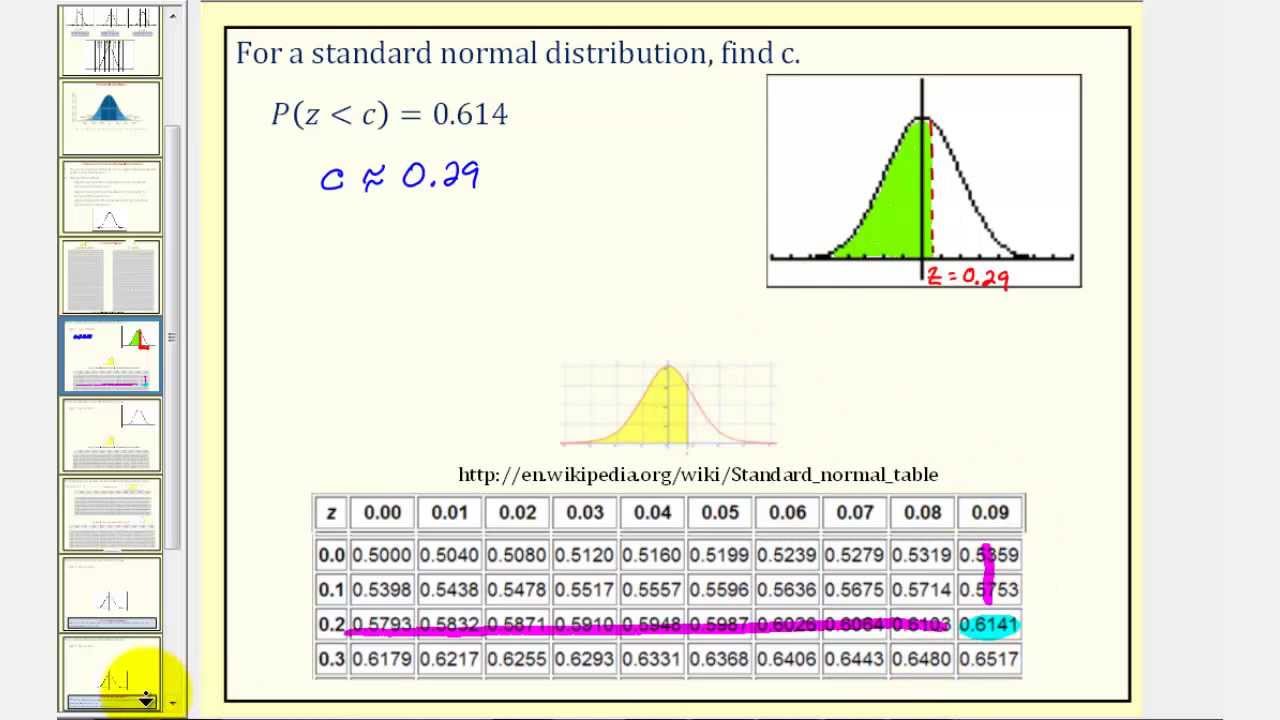
Som you can then easily see that the corresponding area is which translates into % of the standard normal distribution being below (or to the left) of the z-score. How To Use A Z Table To Find The Area To The Right Of A Positive Z Score. Title: z Scores 1 z Scores the Normal Curve Model 2 The normal distribution and standard deviations 3 The normal distribution and standard deviations In a normal distribution Approximately 68 of scores will fall within one standard deviation of the mean 4 The normal distribution and standard deviations In a normal distribution. For example, if the distribution of raw scores if normally distributed, so is the distribution of z-scores. The mean of any SND always = 0. The standard deviation of any SND always = 1. Therefore, one standard deviation of the raw score (whatever raw value this is) converts into 1 z-score unit.

No comments:
Post a Comment